|
Use Internet
Explorer only, other browsers may not show the site correctly
Cambridge University (Emmanuel
College), 10 - 12 April 2013 View proceedings in IEEE Xplore Digital Library: UKSim2008, UKSim2009, UKSim2010, UKSim2011, UKSim2012, UKSim2013 |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Call for Papers Paper Submission Registration Venue/Rooms Social Events
Submission: See above Notification Paper: from 1 Feb Final
Upload into EDAS for checking & Registration (Payment): 20
February Credit Card on EDAS Camera-ready to IEEE server & copyright form: 27 January Conference Chair: Alessandra Orsoni Programme Chair: Adam Brentnall Local Arrangements/ Venue Chair: Richard Cant General Chair: General Co-Chair: Ajith Abraham EUROSIM Liaison Chair Alessandra Orsoni |
Presenters/Session chairs & their
duties Program of papers
to be Presented Conference venue: Emmanuel College, St
Andrew’s Street, Cambridge, CB2 3AP. For those who booked College rooms
collect keys from Porters Lodge. Other
accommodation in Cambridge __________________________________________________________________________________________________________ Scheduled
Papers,
Session Chair Duties Presenters/Session chairs
& their duties Table of Content/page numbers, CD-Label, ISBN etc Conference venue: Emmanuel College, St Andrew’s Street,
Cambridge, CB2 3AP. Other
accommodation in Cambridge Schedule: check your paper is included Write
your paper using these Templates: Word template (MS Word .doc format) And Submit to EDAS http://edas.info Registration Fee: Payment ______________________________________________________________________________________________ Papers are invited on any aspect of modelling and simulation to
be presented at UKSim2013, University of Cambridge (Emmanuel College). The
accommodation, renowned catering and conference facilities are an ideal blend
of modern and historic. The venue offers an especially attractive opportunity
for both professional discussion and socialising. Full Paper (six pages with figures) are invited on any aspect of modelling,
simulation and their applications. Tracks/Themes - Intelligent Systems - Hybrid Intelligent Systems - Soft Computing and Hybrid Soft
Computing - Computational Intelligence - Systems Intelligence - Intelligence Systems - Control of Intelligent Systems - Control Intelligence - e-Science and e-Systems - Robotics, Cybernetics,
Engineering, Manufacturing and Control - Methodologies, Tools and
Operations Research - Bio-informatics and Bio-Medical
Simulation - Discrete Event and Real Time
Systems - Image, Speech and Signal
Processing - Natural Language
Processing/language technologies - Computer Generated Art (images
to be exhibited at the conference and included in the proceedings CD) - Industry, Business and
Management - Human Factors and Social Issues - Energy, Power Generation and
Distribution - Transport, Logistics, Harbour,
Shipping and Marine Simulation - Supply Chain Management - Virtual Reality, Visualization
and Computer Games - Parallel and Distributed
Architectures and Systems - Internet Modelling, Semantic
Web and Ontologies - Mobile/Ad hoc wireless
networks, mobicast, sensor placement, target tracking - Performance Engineering of
Computer & Communication Systems - Circuits, Sensors and Devices Suggested topics (other topics are also welcome): Simulation methodology and practice,
languages, tools and techniques. Models and modelling tools. Data/object
bases. Analytical and statistical tools. Simulators and simulation hardware,
training simulators. Integration of simulation with concurrent engineering,
integrated design and simulation systems. AI, intelligent systems,
agent-based simulation, decision support systems, philosophical issues,
analogies, metaphors, knowledge modelling, acquisition and synthesis of new
knowledge/models, intelligent/adaptive behaviour, man/machine interaction,
control systems. Parallel and distributed simulation, discrete event systems.
Artificial neural networks, computational intelligence. Applications: aerospace; remote sensing;
electronic circuits and systems; communication and networks; business;
management; finance; economics; leisure, games, war/conflict/rebellion
modelling; psychology, cognitive functions, behaviour, emotion, subjectivity;
humanities, literature, semantics modelling/dynamics; biology; medicine;
public health; energy, power generation and distribution, manufacturing;
planning; control; robotics; measurement; monitoring; energy; safety critica1
systems; transportation; structural mechanics and civil engineering, oil and
gas; education and training; military. Exhibitors: manufacturers of software and
hardware, publishers, etc., are invited to apply to exhibit their products. Accepted papers will be published in the IEEE Digital
Library. Selected
papers will be considered for publication in the International Journal of
Simulation: Systems, Science & Technology. The registration fee is $595. This will include a copy of the proceedings,
refreshments and lunch. Accommodation
in College: graduates from Cambridge colleges go on to become leading
world scientists, prime ministers, parliamentarians and top civil servants.
Share the experience of living-in by staying in college rooms. An all
inclusive full-board 3-day package is available for $690, single occupancy.
This includes a meal on the evening before the conference, all
meals/conference dinner on day 1 and day 2
(including conference pre-dinner reception), and breakfast and lunch
on day 3. For those wishing to eat outside, a Bed & Breakfast 3 day
package is available at $470 single occupancy. A limited number of en-suite
rooms is also available on all-inclusive full board basis at $820 for a 3 day
package, single occupancy. Booking and pre-payment is essential, see EDAS Registration. |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Submission Guidelines |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
You are invited to submit: - computer generated art, submit title and
abstract on EDAS as a normal paper then upload the image pdf file only as the
‘full paper’ - proposal to organize a
technical session and/or workshop. Submissions must be
original, unpublished work containing new and interesting results that
demonstrate current research in all areas of modelling and simulation and
their applications in science, technology, business and commerce. The
proceedings of the Conference will be published by the IEEE Computer Society.
The conference is supported/co-sponsored by -
EUROSIM -
European Council for
Modelling & Simulation -
Society for Computer
Simulation Int. (SCS)- Europe -
IEEE UK &RI
Computer Chapter -
Asia Modelling &
Simulation society Submission
implies the willingness of at least one of the authors to register and
present the paper. All papers are to be submitted electronically,- see full
instructions under Paper Submission
below, in PDF or Word format. All
papers and artwork will be peer reviewed by at least three independent
referees of the international program committee. Paper Submission: UKSim2012 is using EDAS for submission and
registration, authors need to: - create an account with
EDAS by clicking on the link below - open the list of
conferences managed by EDAS & find UKSim2012 - click on Submit button on
the right to enter your paper title & abstract - upload file. IEEE Author Kit: emailed to authors on completion of
registration/payment on EDAS. Paper Templates: Word template (MS Word .doc format) Proposals
to organise sessions Authors
of the best papers will be invited to revise and extend their work for
publication in a special issue of the International Journal
of Simulation: Systems, Science and Technology. Conference website: http://uksim2013.info IPC |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Kai Juslin
(SIMS) Esko Juuso
(SIMS) Khalid
Al-Begain (UKSim) Rashid Mehmood (UKSim) Gaius Mulley (UKSim) Miroslav
Snorek (CSSS) Andras Javor (HSS) Franco Maceri (ISCS) Peter Schwartz (ASIM) Charles Patchett (BAE, Warton) Henri Pierreval (FRANCOSIM) Yuri Merkuryev (LSS) Zulkarnay Zakaria (Malaysia) |
Gaby Neumann (ASIM) Hosam Faiq (Malaysia) Hissam
Tawfik (UK) Jiri Kunovský
(CSSS) Azian Azamimi Abdullah (Malaysia) Sanjay Chaudhary (India) Arijit Bhattacharya (Ireland) Atulya Nagar (UK) Gregorio Romero (Spain) Kenneth Nwizege (UK) Kathy Garden (NZ) M Luisa Martinez (Spain) |
Suiping Zhou (Singapore) Mikulas
Alexik (CSSS,EUROSIM President) Borut
Zupancic (SLOSIM) Igor Skrjanc (SLOSIM) Wan Hussain Wan Ishak
(Malaysia) Nitin Nitin (India) Ford Gaol (Indonesia) Philip Sallis (NZ) Martin
Tunnicliffe (UK) David
Murray-Smith (UKSim) Mahdi
Mahfouf (UKSim) Emelio
Jimenez Macias (SPAIN) |
Alessandra
Orsoni (UKSim) Vlatko
Ceric (CROSSIM)Theodoros
Kostis (Greece) Russell
Cheng (UKSim) Miguel
Angel Piera (Spain) Antonio
Guasch (Spain) David
Al-Dabass (UKSim) Jadranka
Bozikov (CROSSIM) Richard Cant (UKSim) Felix Breitenecker (ASIM, SNE) Eduard Babulak (Canada) Siegfried Wassertheurer (ASIM) |
Wolfgang Wiechert (ASIM)S. Wassertheurer (ASIM) Janos Sebestyen-Janosy (HSS) Olaf Ruhle
(ASIM) Zuwairie
Ibrahim (Malaysia) Marius
Radulescu (ROMSIM) Leon
Bobrowski (PSCS) Mojca
Indihar Stemberger (Slovenia) Rosni
Abdulla (Malaysia) Vesna
Bosilj-Vuksic (Croatia) Roland
Wertz (Germany) |
Norlaili
Safri (Malaysia) Nikolaos
V. Karadimas (Greece) Piers Campbell (UAE) Fabian Böttinger
(Germany) K.G. Subramanian (Malaysia) |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Author/ Participant |
Student
Paper (2
authors maximum) |
Student
Participant |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Registration
BEFORE deadline of 20 February IEEE
Members: 5% discount is given to author after presentation at conference |
$595 $30 |
$545 $30 |
$325 |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Registration
AFTER deadline of 20 February IEEE
Members: 5% discount given to author after presentation at conference |
$640 $32 |
$590 $30 |
$350 |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
A minimum of one registration fee is payable for each paper
accepted. When the final version of the paper is uploaded one of the authors should be nominated to attend the conference and present the paper. If this is not done then the organising committee will assume that the first author is the nominated author. The status of the nominated author will determine the registration fee that is payable for that paper. If additional authors wish to attend (and they are not the nominated author for another paper) then an additional registration fee is payable for each such author. Attendees must pay the
registration fee appropriate to their own status. |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Big Data and Real-time Computing Prof Hermann-Hessling Hochschule für Technik und Wirtschaft Berlin hessling@htw-berlin.de The
computing power of processors is increasing exponentially according to
Moore’s law. Over decades, mainly the increase of the clock speed ensured the
raise of the power. However, this development seems to come to an end.
Currently, even notebooks are provided with multi-core CPUs. But also the
amount of stored data is increasing exponentially. Every day new data of the
order of zettabytes are created worldwide. Traditional methods for storing
and maintaining this enormous flood of data seem to be no longer sufficient
anymore. The complexity of the data that are more and more distributed
worldwide, will constitute a considerable challenge for their analysis.
According to Alex Scalay there soon will be produced so many data that they
cannot even be stored anymore. They have to be analysed in real-time. In
science, these enormous developments are considered as hints of a “fourth
paradigm”. In addition of the three fundamental pillars “experiment”,
“theory”, and “simulation”, a fourth pillar “data-intensive science” is
currently established. In
science, measurements are becoming more and more detailed and call for
storing larger and larger data sets. The analysis of the primary data is
accompanied with the generation of secondary data. Primary and secondary
data, together with the analysing software needs to be archived in order
allow for a reanalysis later on. The different phases of a scientific life
cycle are considered in the project “Large Scale Data Management and
Analysis” (LSDMA). Four Helmholtz centres, six German universities (inter
alia HTW Berlin), and the German Climate Computing Centre are cooperating.
The LSDMA project started in 2012 and the initial phase will end on December
31st, 2016. Contrary to similar projects, LSDMA follows a dual ansatz: the
research groups of five “Data Life Cycle Labs” (DLCLs) • “Energy”: SmartGrids, battery research • “Earth and Environment”: climate models and data • “Health”: brain atlas • “Key Technologies”: electron microscope,
nanoscopy • “Structure of Matter”: photon science, heavy ion
physics are supported actively in maintaining their huge
amounts of data, e.g. • (further) development of data formats • connecting existing analysis tools and new
storage systems • development of new interfaces • automatic generation of metadata. The
DLCLs are complemented by a “Data Services Integration Team” (DSIT), that has
the mission to provide tools, services and processes required for the uniform
access to computing and storage resources. This includes access to high
performance storage, replication, organization and archival of data. Uniform
access regardless of the scientific discipline using the service will ensure
an efficient provisioning and support for all participating datacenters. In the
talk he introduces briefly the general challenges of “Big Data”, gives an
overview of the LSDMA project and reports on recent results shown at the
LSDMA spring workshop (March, 11th -12th 2013, DESY, Hamburg). Moreover, he
presents the activities of his working group in real-time computing on
heterogeneous networks (grid / cloud computing) which is likely to have an
impact on the analysis of Big Data.. Biography
*
* * Keynote Speaker- 2 Modelling And Simulation
for Archaeology - Prehistoric Hallstatt Salt Mines Exploration –
Felix Breitenecker1,
Kerstin Kowarik2, Hans Reschreiter2, Gabriel Wurzer3, Niki Popper4, Bernhard Heinzl1,4; felix.breitenecker@tuwien.ac.at 1Institute for Analysis
and Scientific Computing, Vienna University of Technology 3Inst. f. Digital
Architecture and Planning, Vienna University of Technology 2Natural History Museum Vienna; 4dwh Simulation Services, Vienna The prehistoric salt mines of Hallstatt in Austria are the
subject of great interest for archaeologists. Salt mining activities date
back to 1458-1245 B.C. in the Bronze Age. A large amount of archaeological
finds of technical equipment and organic materials (timber, wooden tools,
strings of bast, fur etc.) and the perfect conditions of preservation in the
mines due to the conserving properties of salt allow for a reconstruction of
the working process in the mines. Salt was mined in underground mining
chambers using special bronze picks. The resulting small pieces of salt were
then collected in buckets and transported to the vertical shaft where it was
hoisted to the surface using a wool sack or cloth attached to a linden bast
rope (Kowarik et al. 2012). In collaboration between the Natural History Museum Vienna
and Vienna University of Technology, modeling and simulation is used as
‘virtual experimental archeology’, in order to discuss open questions on use
of mining tools and mining operation strategy. For investigations on use of
mining tools, physical modeling is a very suitable approach for modeling and
simulation, while for mining operation and supply strategies agent-based
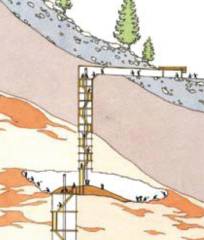
modeling and simulation allows interesting insights. Modelling and Simulation of Mining Tools. Rope pull systems were
used to hoist the broken salt from the mining halls through shafts to the
surface (see figure 1). To estimate and compare the time and strength
requirements for transporting the salt, various options are investigated
using simulation models. An important issue concerns modelling of the rope
guide, for which we consider two possibilities, one with sliding friction on
a log and one with return pulley. Evaluation of the simulation results shows
a significant force requirement for the model with sliding friction,
especially because of the high mass of the rope being the reason for a
limitation regarding the maximum continuous shaft height. Salt was mined using bronze picks. Highly interesting is
the unusual shape of the pick with a typical angle between the shaft and tip
of about 55 to 75 degrees. It is believed that this particular shape was
adapted to the specific working conditions in the Hallstatt mines, especially
since no similar devices have been found at other at archaeological sites.
The small angle does not allow typical circular hacking motion, which is why
it is not yet completely clear exactly how such a pick was used. Modelling
the pick as a rigid body system allows evaluation of possible movement
scenarios (which result from geometrical considerations) regarding energy
demand and momentum.
During mining, burning
sticks of wood served as the only illumination in the mining halls. Burnt down
woodchips were found during excavation in large quantities. The resulting
light intensity by burning woodchips can be estimated by a two- dimensional
discretized model of the hall. Calculations on flames’ oxygen consumption, in
addition to the oxygen demand of the workers, gives information about the
necessary air ventilation and maximum number of workers in the mining halls. Modelling and Simulation
of Mining Strategy. Agent-Based Simulation allows to build a model of the working
processes in the mine in general and in one mining hall (breaking salt,
collecting salt, transporting salt to the shaft), in order to gain insights
into spatial organization, allocation of tasks and workload balance and to
relate the time span of mining to the size of the workforce and the amount of
mined salt. A System Dynamics Simulation can then correlate the size of the
workforce (population dynamics) with food consumption and demand for mining
tools.
References 1. Kowarik, K., Reschreiter, H., Wurzer,
G., 2012. Modelling Prehistoric Mining. In Proceedings of the 7th Vienna
Conference on Mathematical Modelling. February 15-17, 2012, Vienna. (see also
for picture sources). 2. Reschreiter, H., Kowarik, K., 2009. The Bronze Age. In: Kern et al. Kingdom of Salt: 7000 Years of Hallstatt. Vienna: VPA3, Natural History Museum Vienna, 48-64. Biography
News Europe and running benchmarks on M&S approaches. Felix Breitenecker is
author of five books and of about 300 scientific publications in the area of
modeling and simulation. Recent research activities include physical modeling
(port-based DAE modeling), elearning with/for modeling and simulation,
modeling and simulation in physiology and health care systems. Felix Breitenecker is
active in various simulation societies and simulation activities in Europe.
At present he is president of ASIM, the German simulation society, and board
member of EUROSIM, the Fderation of European Simulation Societies. Vienna Univ. of Technology RG Mathematical Modelling and Simulation Wiedner Hauptstrasse 8-10 A-1040 Vienna, AUSTRIA Phone: +43(0)15880110115
Fax: +43(0)15880110199 E-mail: felix.breitenecker[at]tuwien.ac.at
* * * Keynote Speaker-3 Semantic Systems Modeling and Monitoring for Real Time Decision Making: Results and Next Steps within the Greek Cyber Security Center of
Excellence. Dr
Vasilis Tsoulkas Center for Security Studies (KEMEA),
Athens, Greece. Co-contributors: Dimitris
Kostopoulos , Vasilis Tsoulkas, George Leventakis, Prokopis Drogkaris and
Viky Politopoulou. Keywords: Critical Infrastructures,
semantic modeling, Semantic reasoning and risk analysis, core system
ontologies, stream reasoning and event processing, DST user interfaces. Our
presentation is comprised of two interconnected sections: Firstly we will
present results recently delivered and approved by the European Commission
regarding the EC FP-7 project SERSCIS (Semantically Enhanced Resilient and
Secure Critical Infrastructure Services). http://www.serscis.eu. These focus on the following issues: · The SERSCIS Proof of Concept
Architecture with the
associated technical limitations during the initial implementation phase. In
the sequel the concept and advantages of introducing in a later realization
stage modern stream reasoning techniques and in particular the data
processing steps in a stream reasoner for real time threat classification and
estimation. · The Semantic monitoring
architecture with an
emphasis on the Semantic Monitoring and Reasoning Components as well as the
so called “Behavioral Analyser” capable of mapping the streaming monitoring
data into semantic assertions about the presence or absence of a threat
against a Critical Infrastructure. · The Semantic Reasoning Process in combination with its
sequential reasoning computational steps.
Moreover and in conjunction
with the A-CDM approach (Airport – Collaborative Decision Making) which is
the European Initiative for optimizing European Air Traffic Management across
European airports, validation results will be provided. In this direction
some asset threat cases will be analyzed for the SERSCIS Proof of Concept
comprised of: Attacks - Induced behaviors – Controls. Semantic modeling issues will be presented
in conjunction with the final prototypical Decision Support Tool
Interfaces. In the second part the recently launched Greek Cyber
Security Center of Excellence will be introduced
including: Its national and European dimension, it’s educational and
awareness role to societal needs concerning cyber-crime as well as planned
research activities and efforts related to Fast Intrusion Detection
algorithms and the use of Semantics dynamic modeling approaches towards state
of the art cyber – security tools.
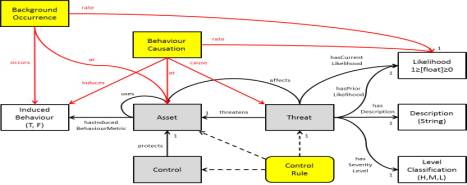
Figure 1. Proof of concept:
complete core ontology
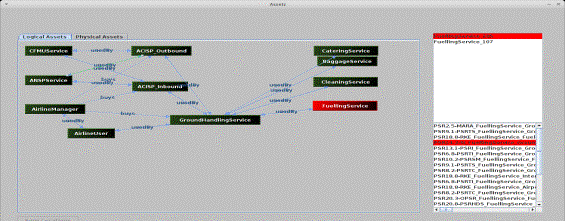
igure
2. Decision
Support Tool screenshot of logical assets
with threat alarm. References 1. M.
Surridge, A. Chakravarthy, M. Hall-May, R. Nossal: “SERSCIS: Semantic
Modelling of Dynamic, Multi-Stakeholder Systems,” Second SESAR Innovation
Days, 27th-29th November 2012. 2. Semantically
Enhanced Resilient and Secure Critical Infrastructure Services, EC FP7
Project 225336, 2008 – 2012. (http://www.serscis.eu) 3. Deliverable
D5.2: Decision Support Tools: Full Prototype Implementation, 22/01/2013. Lead
Author: Vasilis Tsoulkas. Contributors: D. Kostopoulos, N. Nikitakos, M.
Surridge, W. Chen, T. Leonard, M. Hall-May. Internal Reviewer: M. Surridge 4. D.F.
Barbieri, D. Braga, S. Ceri, E.D. Valle and M. Grossniklaus, “Incremental
Reasoning on Streams and Rich Background Knowledge,“ in ESWC, Heraklion,
Greece, 2010. 5. Kostopoulos,
D., Leventakis, G. Tsoulkas, V., and Nikitakos, N., “An Intelligent Fault Monitoring
and Risk Management Tool for Complex Critical Infrastructures: The SERSCIS
Approach in Air-traffic Surface Control,
In: 14th International Conference on Computer Modelling and
Simulation (UKSim), March 2012, Cambridge, UK (IEEE Computer Society). Biography
In 2010 he joined the Center for Security Studies (KEMEA)/
Ministry of Citizen Protection as a research engineer where he is responsible
for the implementation of R&D EU and national funded programs in the
areas of: Protection of Critical Infrastructures using advanced modeling
tools, Cyber – Physical security of interconnected infrastructures such as
the smart grid and smart metering sub-systems for power utility services as
well as end – user requirements and implementation of Future Internet (FI-WARE) applications for
safer and more secure cities. Since
2010 he is appointed to the position of senior visiting fellow, Dept. of
Mathematics and Engineering Sciences, City University, London, UK (three year
term). He has published in scientific journals, conferences and delivered several invited key – note lectures and special
tutorials at the intersection of control – communications and systems
integration. His recent interests include risk/threat assessment and
classification, semantics and ontology engineering with applications to
security of Critical Infrastructures and semantically driven
tools for Decision Support Systems. Also applications of Complex Event Processing and Stream
Reasoning Algorithms for large volume event analytics. He is currently working on the project reported here and plans to present state of the Art results, tools and methods from a FP-7 European Funded Project called SERSCIS. *
* * Keynote Speaker-4 Towards 2020 Computing Prof. Frank Wang Head of School of Computing, University of Kent Canterbury, UK Chair, IEEE Computer Society, UKRI Chapter Towards 2020 Computing targets the next
generation computing paradigms and their applications. We have been working
on Cloud Computing, Grid Computing & Internet II for many years. A
developed Cloud/Grid Computing platform conforms to the Internet standard and
can universally accelerate Office/Database/Web/Media applications by a factor
up to ten. This work won an ACM/IEEE Super Computing finalist award. We will
also report our research on Green Computing, Brain Computing and Future
Computing. Biography
*
* * Keynote Speaker-5 Artificial Intelligence
and Emotion from Natural System Prof Dong Hwa Kim Department of Instrumentation and Control Engineering Hanbat National University South Korea koreahucare@gmail.com Keywords: (Immune, Genetic Algorithm, Particle Swarm Optimization,
and Bacterial Foraging, Its Hybrid system, and Emotion System) This
lecture deals with intelligent method using natural system such as immune
system, genetic algorithm, particle swarm optimization, bacterial foraging,
and its hybrid system and application to real system. Immune system, PSO
(Particle Swarm Optimization), BF (Bacteria Foraging), and hybrid system can
have strong optimization function to survive for their life. First, this lecture describes research
background about immune network based intelligent algorithm, PSO based
intelligent algorithm, bacteria foraging based intelligent algorithm, and the
characteristic of novel algorithm fusioned by their algorithm. This one also
illustrates motivation and background that these algorithms should be applied
to in the industry's automatic system. Second, this lecture illustrates immune
algorithm and applied to various plant to investigate the characteristics and
possibility of application. As the detailed description, immune algorithm
will described by studied material to investigate possibility of application
to plant. It suggests condition for disturbance rejection control in AVR of
thermal power plant and introduce first into tuning method of its controller.
In
the conventional genetic algorithm, it takes a long time to compute and could
not include a variety of information of plant because of using sequential
computing methods. That is some problem with making a artificial intelligence
for optimization. In this lecture, by means of introducing clonal selection
of immune algorithm into computing procedure, it will be showed advanced
results. That is, it can be calculated simultaneously necessary various
information, transfer function, time constant, and etc., for plant operation
condition. Therefore, computing time is about 30% shorter than that of the
conventional genetic algorithm and 10.6% smaller in overshoot when it is applied
to controller. This
lecture will introduce parameter estimation method by immune algorithm for
obtaining model of induction motor. It will suggest immune algorithm based
induction motor parameter estimation to obtain optimal value depending on load
variation from these parameters. Also,
this lecture will introduce about intelligent system using GA-PSO. It will
introduce Euclidean data distance to obtain fast global optimization not
local optimization by means of using wide data and suggests novel hybrid
system GA-PSO based intelligent tuning method that genetic algorithm and PSO
(Particle Swarm Optimization) is fusioned. To
prove this effectiveness, four test functions is used and results of
Rosenbrock function, one of four test functions, converges at 20 generations
in GA-PSO and at 40 generations in genetic algorithm, as result GA-PSO
reveals faster running time than that of GA. The
suggested method is applied to tuning of automatic controller for terminal
voltage regulation of AVR (automatic Voltage Regulator) of thermal power
plant. Results reveal best response at 100 generations and results show
6.8331% error in GA, 5.3828% error
(78.8%: reduced) in GA-PSO, in case of overshoot. In case of steady state error,
results illustrate reduced error with 0.0028% error (16.4%: reduced) with
0.0171% in GA and 0.0143% in GA-PSO. In settling time, it represents
0.557(sec) in GA and 0.3989(sec) in GA-PSO and it reduce to 0.159(sec)
(28.5%) by using GA-PSO. In the case of rise time, results shows 0.2037(sec)
in GA and 0.2639(sec) in GA-PSO and tuning results are better than that of
conventional method. This lecture shows novel hybrid system
structured by GA-BF that firstly search wide area by GA and secondly optimize
parameters precisely by BF to enhance divergence speed and optimal accuracy,
and prove effectiveness of the suggested hybrid system on various test
function. In Rosenbrock function, GA converges at 40generations and GA-BF has
already done at 5 generations. That means the suggested hybrid system shows
faster response of 35 generations. When this suggested hybrid system is
applied to AVR (Automatic Voltage Regulator),
there is no overshoot and fast settling time. In induction motor vector PI
control system, as error of speed following efficiency is However, we have some questions why we
have to study not introducing emotion function because emotion function can give
an impact on decision making as they mentioned earlier. So, this lecture will
mention how we can research for artificial intelligence and robot by using
studied materials up to now. Especially, robots are
becoming more and more ubiquitous in human environments as emerging
technology for economic growth. Artificial intelligence will be decided by
our ability to express effectively human’s mind such as intelligence and
emotion. That is, emotion-inspired mechanisms will deal with importance for
autonomous robots in a human environment, and also related works may be
studied. Of course, the cognitive
component is important for perceiving and interpreting events. To implement
emotion function in robot, there are several approaches to soft computing and
control algorithm to control effectively robot. However, many of them do
not deal with emotion function in their soft computing algorithm. So, at this
point, fusion of soft computing and emotional function should be introduced
into the research method and real control system such as, robot, ICT, design,
and so on. Herein, we are going to develop the
corresponding fusion algorithms or models with learning algorithms including
emotion function. Next, applications of these soft computing-based AIS
(Artificial Intelligence Soft computing) in driver and expression system
should be considered as well as analyzed. Performance comparisons between the
conventional methods and new solutions should be made for safety and real
artificial intelligence. Biography
Professor. Dept. of Instrumentation and Control
Engineering Hanbat National University, 16-1 Duckmyong dong Yuseong gu
Daejeon, South Korea 305-719. Contact: Office Phone: 82-42-821-1170, Cell phone:
82-10-8958-1175, 82-10-4899-1170 Fax: 82-42-821-1164, Department Office:
82-42-821-1165 Homepage: http://hucare.org, Email: koreahucare@gmail.com, kimdh@hanbat.ac.kr, worldhucare@yahoo.com Education Ph.D: Dept. of Electronic Engineering, Ajou
University in Korea Ph.D: Dept. of Computational Intelligence and
Systems Science, TIT (Tokyo Institute of Technology, K. Hirota Lab.), Tokyo,
Japan. (Thesis Title: Genetic Algorithm Combined with Particle Swarm
Optimization/Bacterial Foraging and Its Application to PID Controller Tuning) Advanced Program for International Conference
(Fall Semester, 2006), Hallym Institute of Advanced International Studies Ph.D course, Graduate School International, Korea
University, Sept. 2007- Work Experience Prof., Dept. of Instrumentation and Control Eng.,
Hanbat National University, March 2, 1993- Now President, Institute of Korea HuCARE (President of
Hu-CARE (Human-Centered Advanced Technology Research/Education), Nov. 2009- EU-FP NCP (ICT) in Korea, April 29,2011- Korea Atomic Energy Research Institute, Nov.,
1977-March, 1993. Korea-Hungary Joint Work : Aug.1,2010-Feb.28,2011,
Participation in the research of Robot motion related topics of the ETOCOM
project(TAMOP4.2.2-08/1/KMR-2008-2007) including consultation with research
staff members and giving related lectures) President, Daedeok Korea-India Forum, March 1,
2010 – Now. Vice President, Daedeok Korea-Japan Forum, March
1, 2010 – Now. President of Science Culture Research Institute,
Korea Science Foundation, Sept. 8, 2006 - Jan. 31, 2008. Vice-president of the recognition board of the
world congress of arts, sciences and communications, IBC, Sept. 1, 2007, UK. Marquis Who’s Who selected great minds in 21
Century, Aug. 2007/2008/2009. ABI 200 International Scientist, Publishing in
2008. Great minds of 21 Century to dedication in IBC,
2008. UNESCO-APEC Asia Region Forum Held, Nov. 21, 2007. Korean Science Forum Held, Oct. 22, 2007. Science and Technology forum of the deputy Prime Minister of Korean Science and Technology, Operation, Aug. 1, 2006 – Nov. 30, 2007. (8 -round) *
* * Invited Speaker-6 The Inevitable ‘Simulacra
and Simulation’ Dr Zaliman Sauli University of Malaysia in Perils Malaysia The title above has been chosen from work by Jean Baudrillard (1981), written in French, whom was seeking to address the real reality being replaced by humans in their daily life. The advent of multiple human activities since the dawn of civilization has chiselled simulation into our daily life. This has developed to the extent where the simulated entity has been taken into reality, differentiating it would be a status of quandary. For an instance everyone or most of us have a time piece worn on the wrist, the time shown there is the simulated version representing the reality. Simulation
has infiltrated many aspects of technology, and the advantages coupled with
its importance are undeniable. Ranging from medical, biological, automotive,
aeronautical, civil construction, mining, sports, management, finance,
fashion, warfare, navigation, electronics niches, these are just to name a
few. This cornucopia seems to be never-ending, and the catalyst is the
technology advancement in each field. The level of relationship correlation
is astronomical and at nano-world, this has undoubtedly stamped the
inevitable simulation at every aspect of human life. Medical field has been one of the major beneficiary in the advent of simulation to this field. Surgical circle especially have reduced the high risk surgeries to minimal risk, realistic haptic feedback in a surgical environment simulation has brought major improvements. Delicate intrinsic surgeries have been improved drastically with the simulator training provided to the medical personals. The design and simulation of insertion tools into human body were also developed here, the stent for an example used in artery blockage reduction is one of this beneficiaries. Fittings of metal bone insertions, have to be simulated for its adaptability prior to surgical insertion. The contribution in this niche is undeniable, health industry has benefited with varied simulation works. The warfare ramification into complex divisions and its taste for perfect combat entity, has made simulation into an important tool. War-game and shooting trials have made this realistic simulators even to be marketed as games, tactical and entertainment manipulation. Flight simulators have perfected flying even with an airplane which has minimal aerodynamic compatibility and also the support of electronics. In the field of electronics, simulation has contributed immensely in major monetary savings. Material choice, process optimisation, thermal management, circuitry design, interconnection advancement, package reliability and product robustness have all been developed and simulated prior to actual production. Man-hour, material cost, process cost, equipment usage and more costing have been saved here, thus also indirectly speeding up the technology advancement. Simulation is here to stay, the inclusiveness into human life is inevitable. We have gained at all angles of the technology advancement, and outputs to assist mankind. From the unreal to reality has been simulation’s fundamental contribution. The quote ‘for it is with the same imperialism that present-day simulators try to make the real, all the real, coincide with their simulation models’ from Simulacra and Simulation of Jean Baudrillard (1981). Biography
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Papers to be Presented, Final, 8pm
Saturday 6 April. UKSim2013, Scheduled Papers: 108
+ 6 Keynotes/Invited speakers
(Published: 144)
Requests:
B1: day 1 or 2; B2 same day as U11, I3 day 1
or 2; K3 day 1 or 2; P1 day 1 or 2;
U1 day 1 or 2; Y1 day 2 or 3; Z3 day
2 or 3; U7 day 1; Q13 day 2 or 3; P4
with U7 on day1; F1 on day 3; Q2 on day-3 Last minute additions: (not in
Abstracts book, on Door Sheet only) V4 * * *
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||














 Dong
Hwa Kim, Ph.D.
Dong
Hwa Kim, Ph.D.